Java Save Text to File Example
A demo file on the desktop named 'gfg.txt' is used for reference as a local directory on the machine. Creating an empty file before writing a program and give that specific path of that file to the program.
Methods:
- Using writeString() method of Files class
- Using write() method of Files class
- Using writer() method of Filewriter class
- Using write() method of Bufferedwriter class
- Using write() method of PrintWriter class
Let us discuss every method individually by implementing the same via clean java programs to get a fair idea of working on them.
Method 1: Using writeString() method of Files class
The writeString() method of File Class in Java is used to write contents to the specified file. 'java.nio.file.Files' class is having a predefined writeString() method which is used to write all content to a file, using the UTF-8 charset.
Syntax:
Files.writeString(path, string, options)
Parameters:
- Path: File path with data type as Path
- String: A specified string that will enter in the file with a return type string.
- Options: Different options to enter the string in the file. Like append the string to the file, overwrite everything in the file with the current string, etc
Return Value: This method does not return any value.
Procedure:
- Create an instance of the file.
- Call the Files.writeString() method with an instance, string and characters set.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Path path
= Paths.get( "C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\gfg.txt" );
String str
= "Geeks for Geeks \nWelcome to computer science portal \nHello Geek" ;
try {
Files.writeString(path, str,
StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.print( "Invalid Path" );
}
}
}
Output:
Geeks for Geeks Welcome to computer science portal Hello Geek
Method 2: Using write() method of Files class
java.nio.file.Files class is having a predefined write() method which is used to write a specified text to the file.
Procedure:
- Create an instance of the file.
- Convert the string into a byte array by using string.getBytes() method.
- Lastly call method namely Files.write() with file instance and the byte array.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Path path
= Paths.get( "C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\gfg.txt" );
String str
= "Geeks for Geeks \nWelcome to computer science portal \nHello Geek!" ;
byte [] arr = str.getBytes();
try {
Files.write(path, arr);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.print( "Invalid Path" );
}
}
}
Output:
Geeks for Geeks Welcome to computer science portal Hello Geek!
Method 3: Using writer() method of FileWriter class
Filewriter class is used to write some data on file. This is a simple way of writing the data on file.
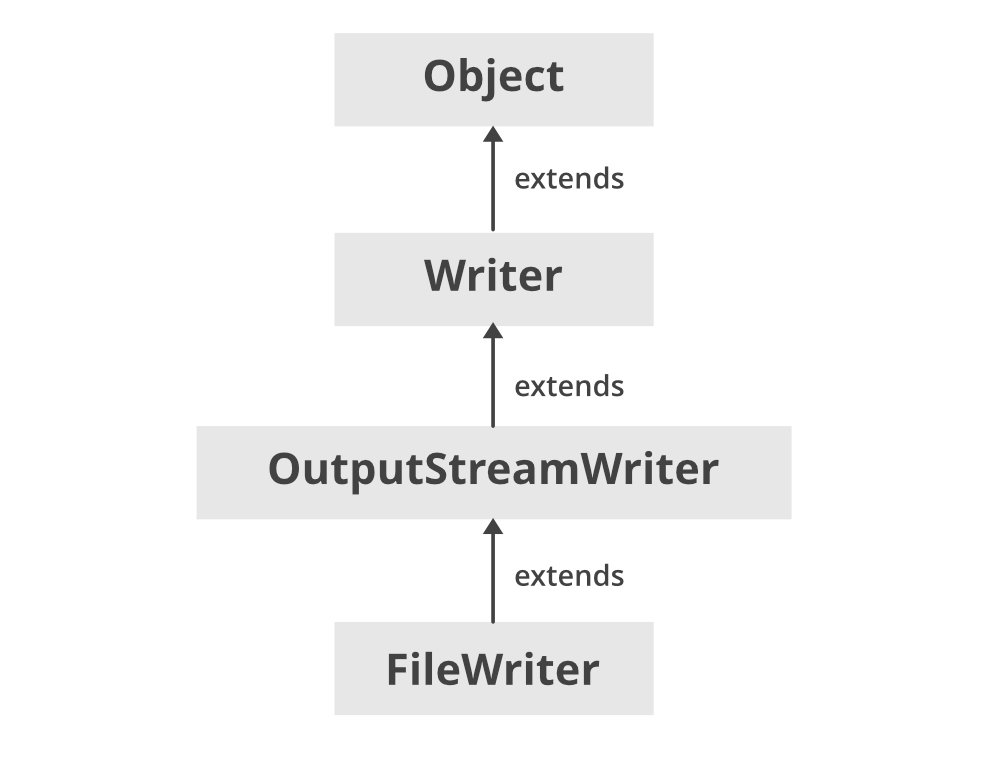
Procedure:
- Create an instance of the file.
- Passing the file instance into filewriter.
- Now call writer() method over a filewriter with string data.
- Flush the file resource.
- Close the file resource.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GFG
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
File path = new File( "C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\gfg.txt" );
FileWriter wr = new FileWriter(path);
wr.write( "Geeks for Geeks \nWelcome to computer science portal \nHello Geek!!" );
wr.flush();
wr.close();
}
}
Output:
Geeks for Geeks Welcome to computer science portal Hello Geek!!
Method 4: Using write() method of BufferedWriter class
BufferedWriter class basically provides a buffer for writing instance. We can wrap some other writers like PrintWriter and FileWriter into BufferedWriter. BufferedWriter is very efficient for doing multiple write operations on file & writing multiple files. BufferedWriter is very efficient than Filewriter.
Procedure:
- Create an instance of the file.
- Declare the stream with filewriter.
- Call write() method on stream with string data.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Path path
= Paths.get( "C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\gfg.txt" );
String str
= "Geeks for Geeks \nWelcome to computer science portal \nHello Geek!" ;
byte [] arr = str.getBytes();
try {
Files.write(path, arr);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.print( "Invalid Path" );
}
}
}
Output:
Geeks for Geeks Welcome to computer science portal Hello Geek!!!
Method 5: Using write() method of PrintWriter class
PrintWriter class is an extension of writer class. PrintWriter class is used to write the string data on file using the write() method.
Procedure:
- Create an instance of the file.
- Create a stream of PrintWriter and pass the file instance into it.
- Call the write method with data.
- Flush the stream.
- Close the stream.
Example
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws FileNotFoundException
{
File path
= new File( "C:\\Users\\HP\\Desktop\\gfg.txt" );
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(path);
pw.write(
"Geeks for Geeks \nWelcome to computer science portal \nHello Geek!!!!" );
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}
Output:
Geeks for Geeks Welcome to computer science portal Hello Geek!!!!
whittemorealed1977.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-program-to-save-a-string-to-a-file/
0 Response to "Java Save Text to File Example"
Post a Comment